Content
Recurrent Neural Networks
Attention Mechanism
Transformer Architecture
An Introduction
by
Department of Aerospace Engineering,
Indian Institute of Space science and Technology,
Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala - 695547
2025-10-19
Recurrent Neural Networks
Attention Mechanism
Transformer Architecture
Sequence to single output processing
Sequence to Sequence mapping
RNNs take two inputs at each timestep
Output of RNNs can be either immediate (output for each timestep input) or culminated (single output at end of sequence)
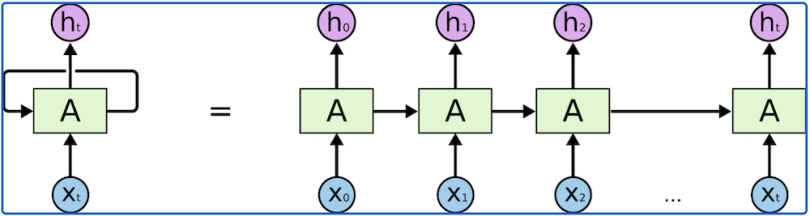
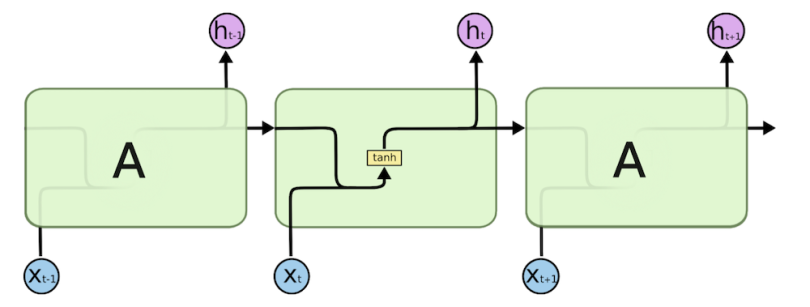
Slow to train: processing each input sequentially
Long sequences lead to vanishing gradient: its memory is not strong to interpret old connections
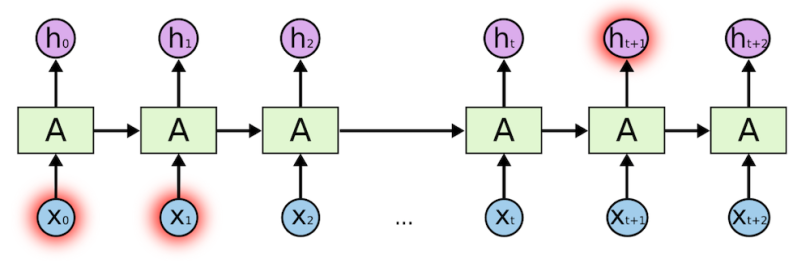
To overcome the vanishing gradient problem
LSTM: Long Short-Term Memory units. GRU: Gated Recurrent Units.
Memory gates: input,forget and output.

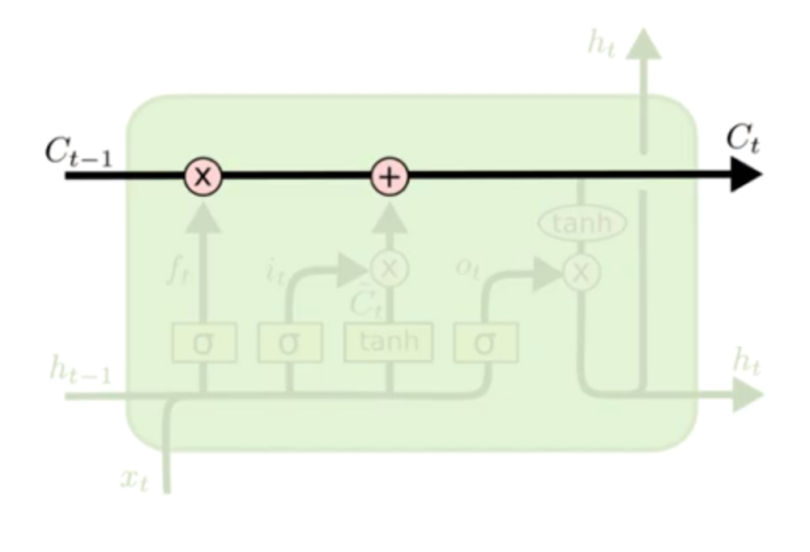
Still LSTMs and GRUs facing difficulty to interpret long sequences like encountered in LLMs (when elements are distant from one another)
Example:
Sequential Networks (RNNs and its variants) can fill this phrase “The clouds are in the —-”
But they may not interpret and fill this phrase
“I grew up in Germany with my parents, I spent many years there and have proper knowledge about their culture. That’s why I speak fluent —–”
To induce contextual information on each element of the input sequence
Let the input sequence of embedded words be \[ \mathbf{X} = \left[\mathbf{x}_1,\dots,\mathbf{x}_n\right]^T \in \mathbb{R}^{n\times d_{model}} \]
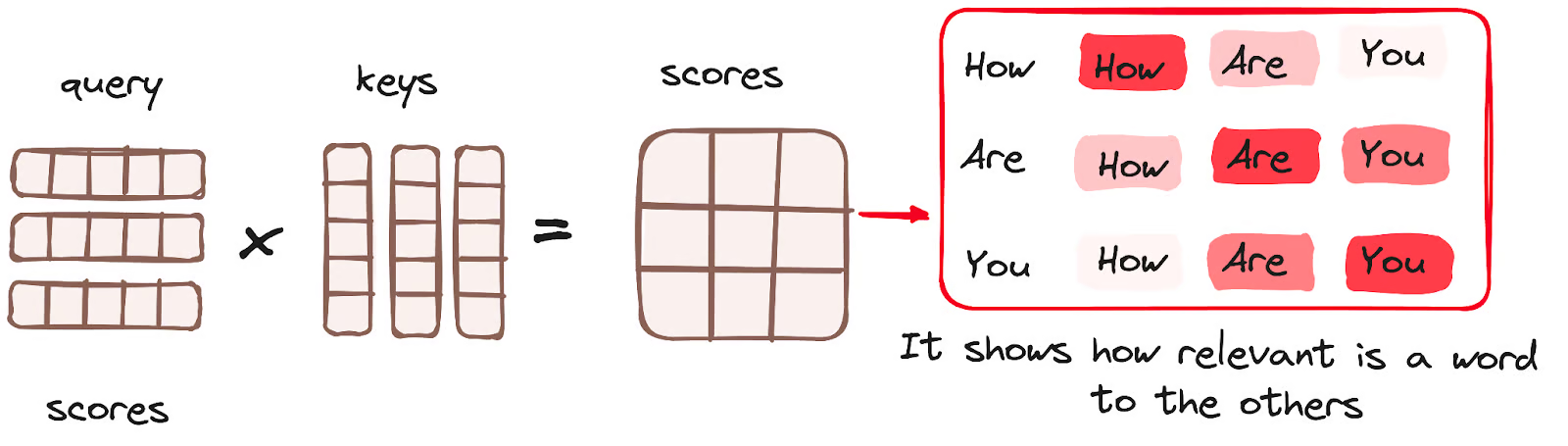
Now, each input token \(\mathbf{x}_i\) is projected linearly into three different spaces. \[ \mathbf{Q} = \mathbf{X}\mathbf{W}_Q, \ \ \ \mathbf{K} = \mathbf{X}\mathbf{W}_K, \ \ \ \mathbf{V} = \mathbf{X}\mathbf{W}_V \]
Where,
The attention output is computed as \[ \mathbf{Z} = \text{Attention}(\mathbf{Q},\mathbf{K},\mathbf{V}) = \text{softmax}\left(\frac{\mathbf{Q}\mathbf{K}^T}{\sqrt{d_{model}}}\right)\mathbf{V} \]
Where,
The attention output, \(\mathbf{Z}\in\mathbb{R}^{n\times d_{model}}\) is a new representation of \(\mathbf{X}\) where each token’s new embedding contains information aggregated from all other tokens.
Goal of attention layer is to mix the contextual information across all tokens efficiently.
The attention decoder RNN takes in the embeddings of the <END> token, and an initial decoder hidden state hinit to produce new hidden state vector h4. Output is discarded.
Attention step h4 \(\to\) context vector C4.
h4 and C4 are concatenated and passed through feedforward NN to get final output of 4th timestep and the process is repeated
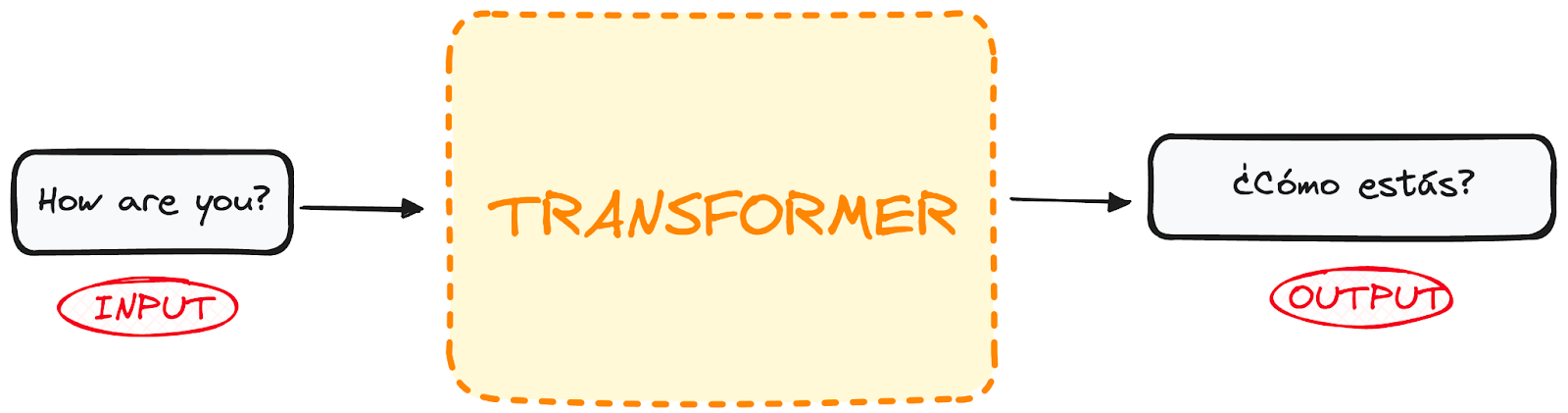
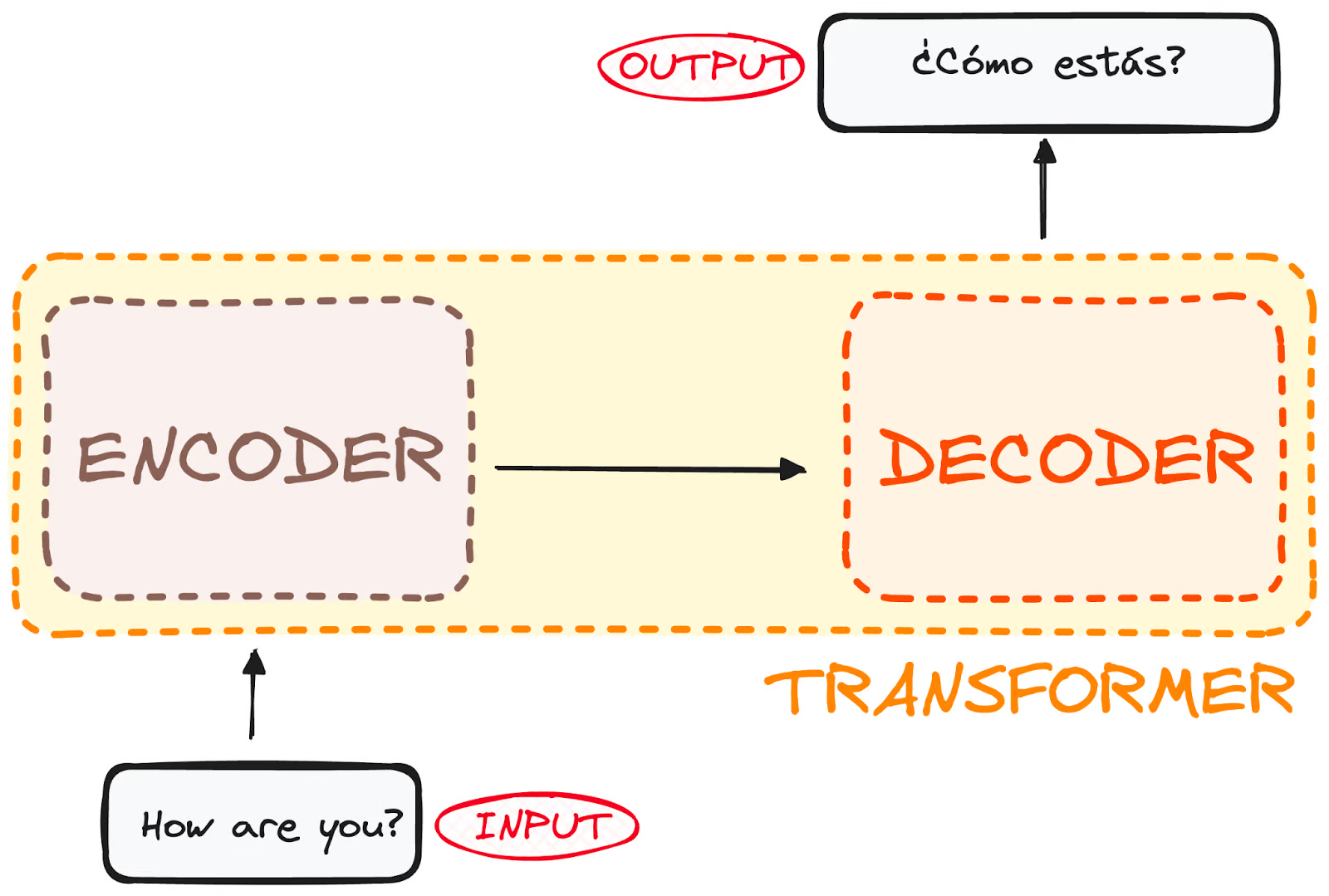
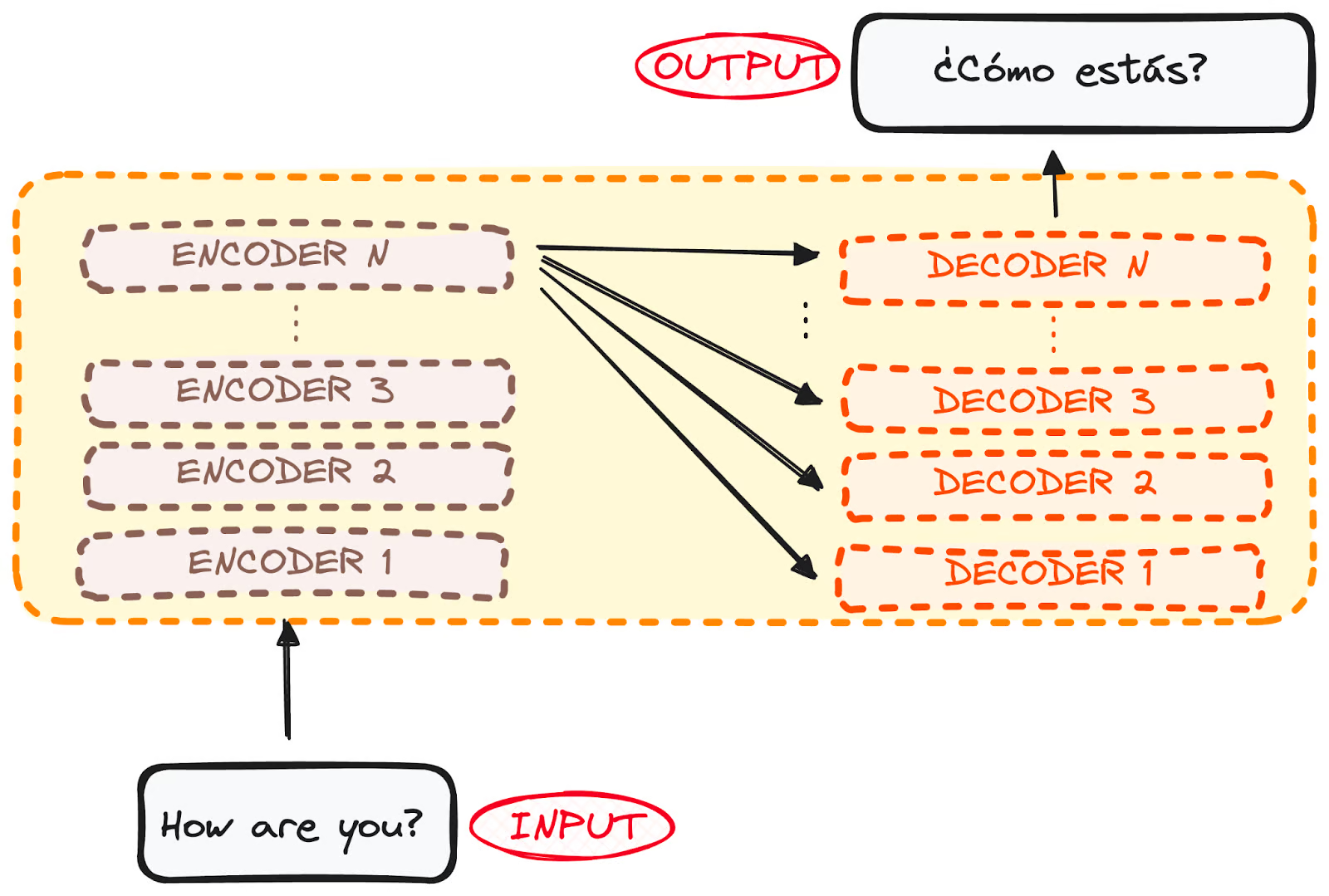
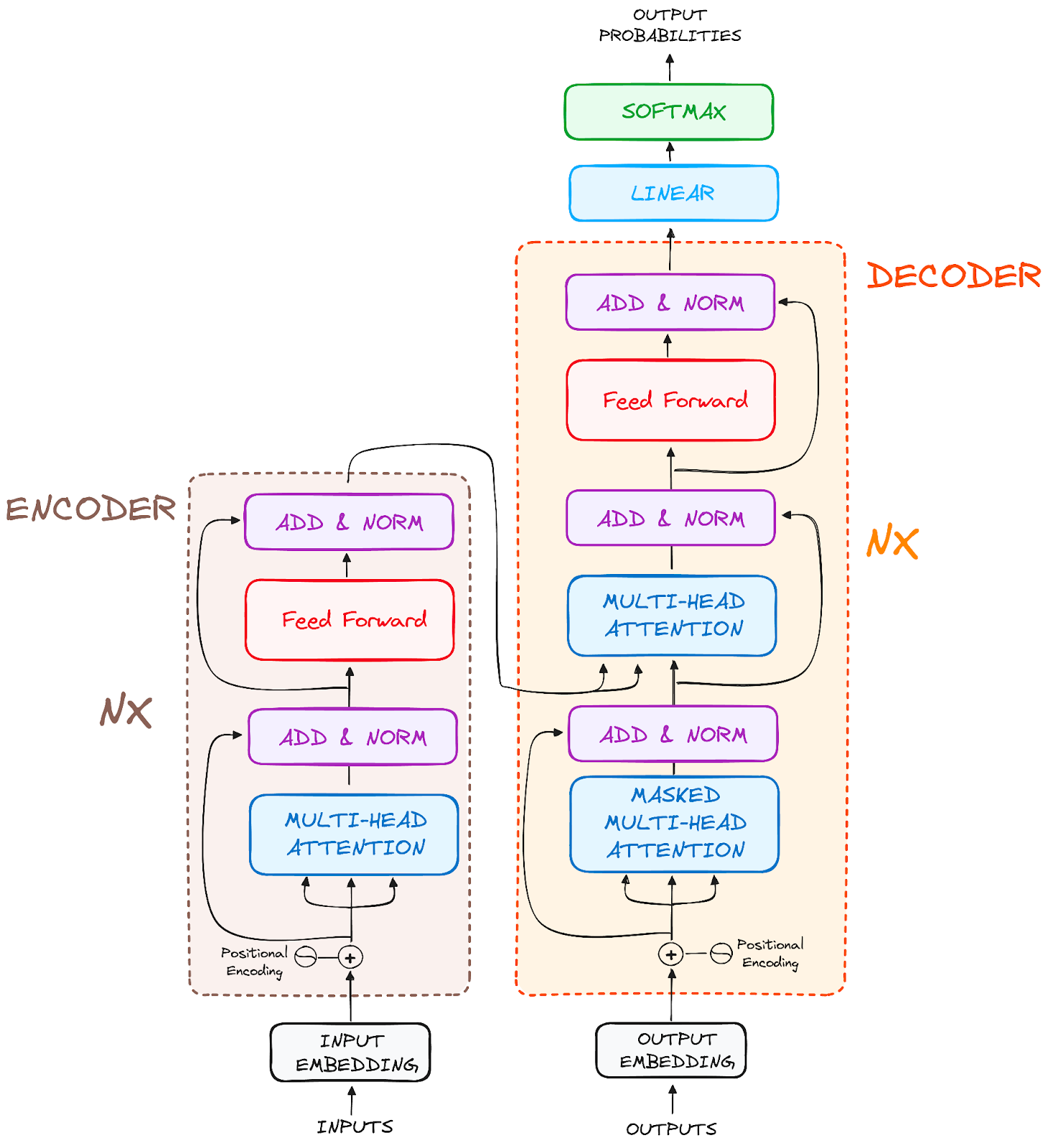
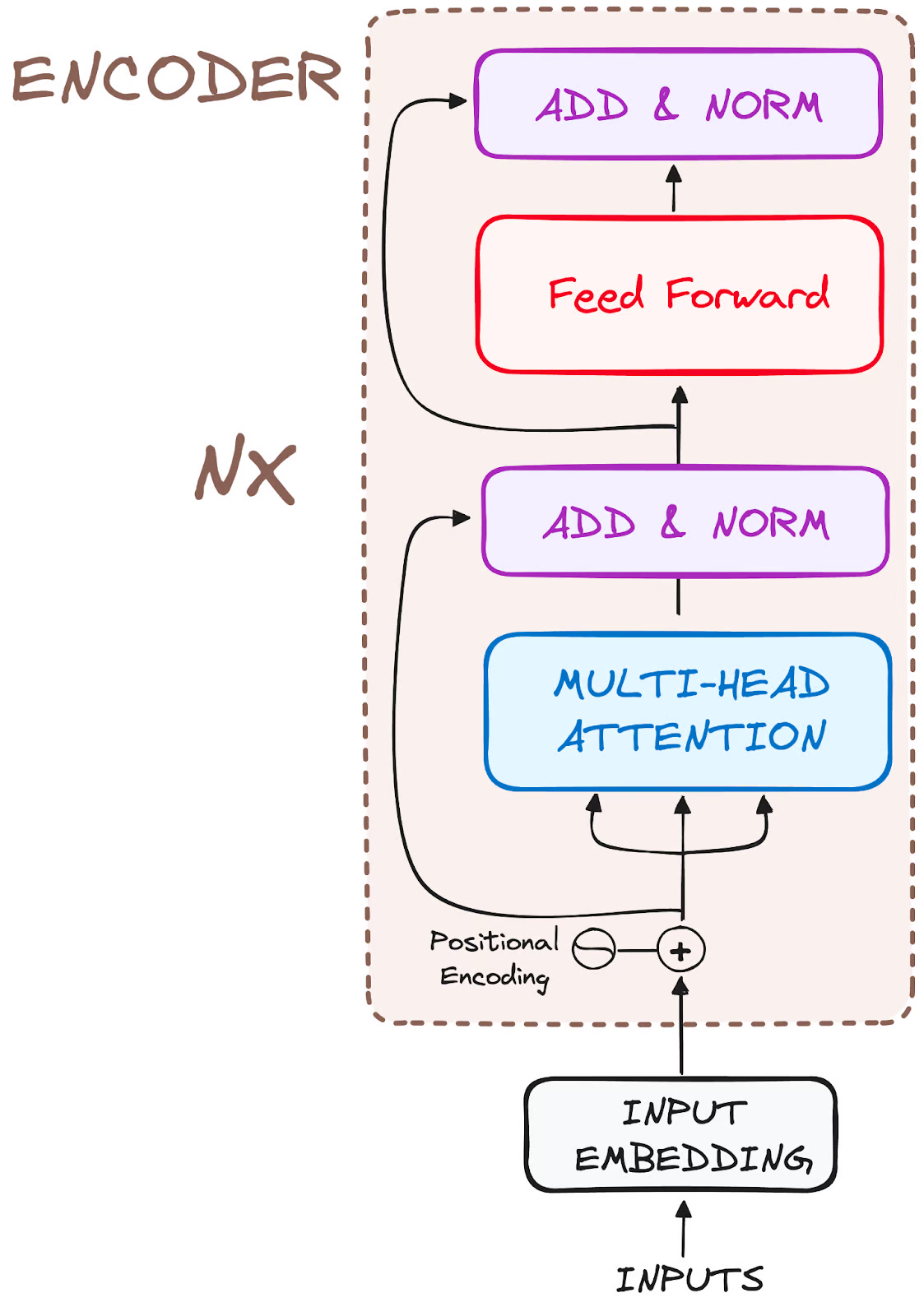
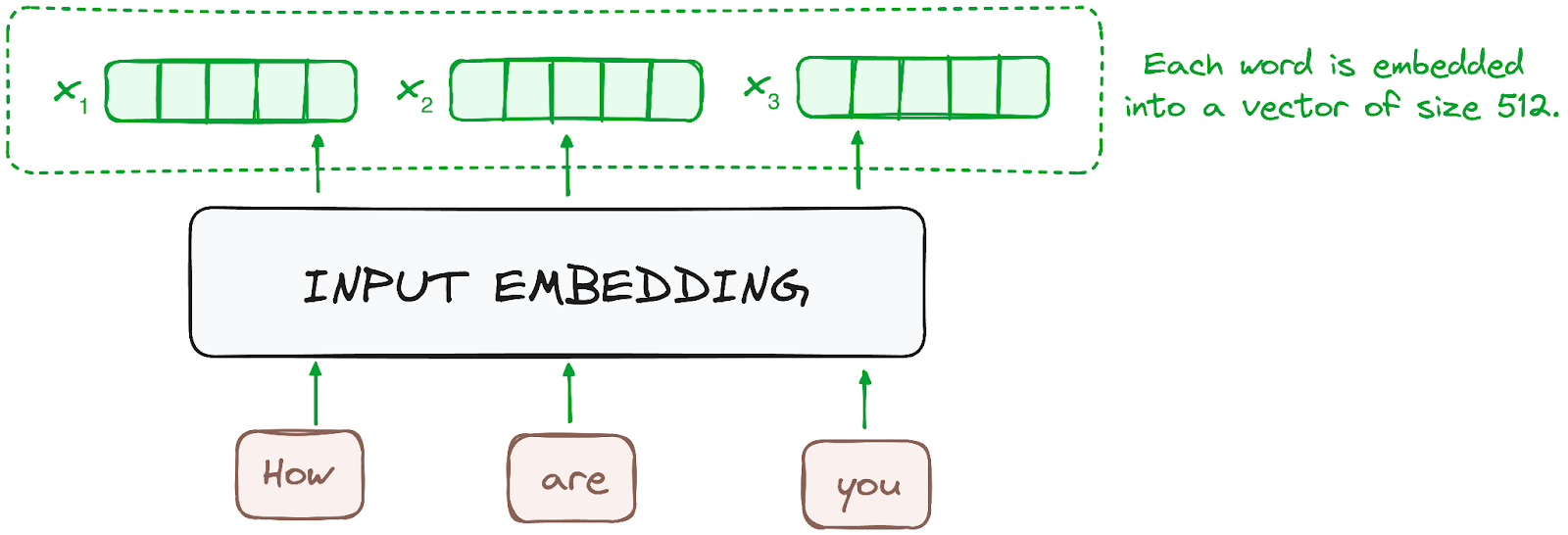
Transformers do not have recurrence mechanism like RNNs
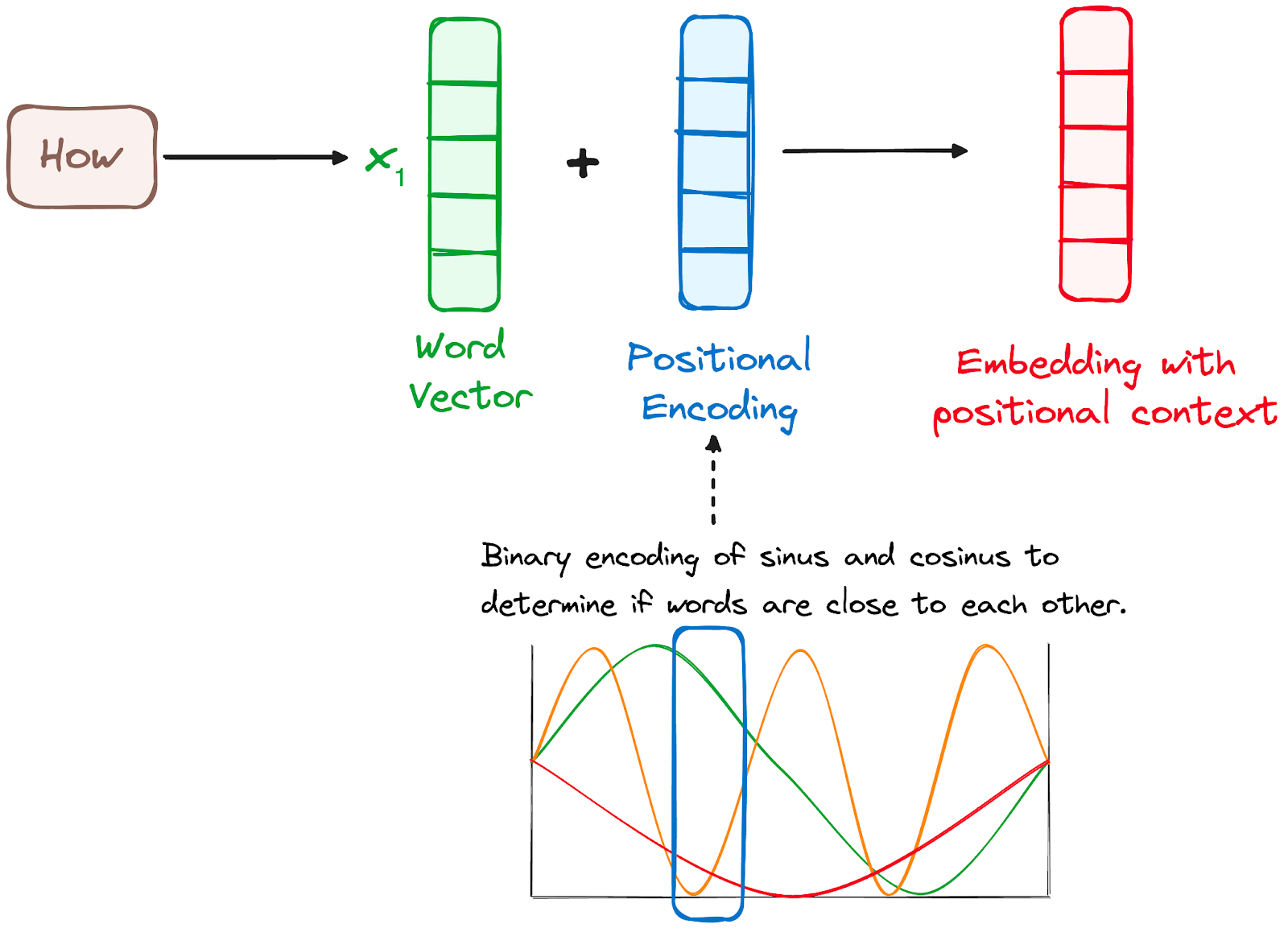
Positional encodings are added to the input embeddings to provide each token’s position information
Position vectors are generated using various sines and cosines combinations (for any sequence length)
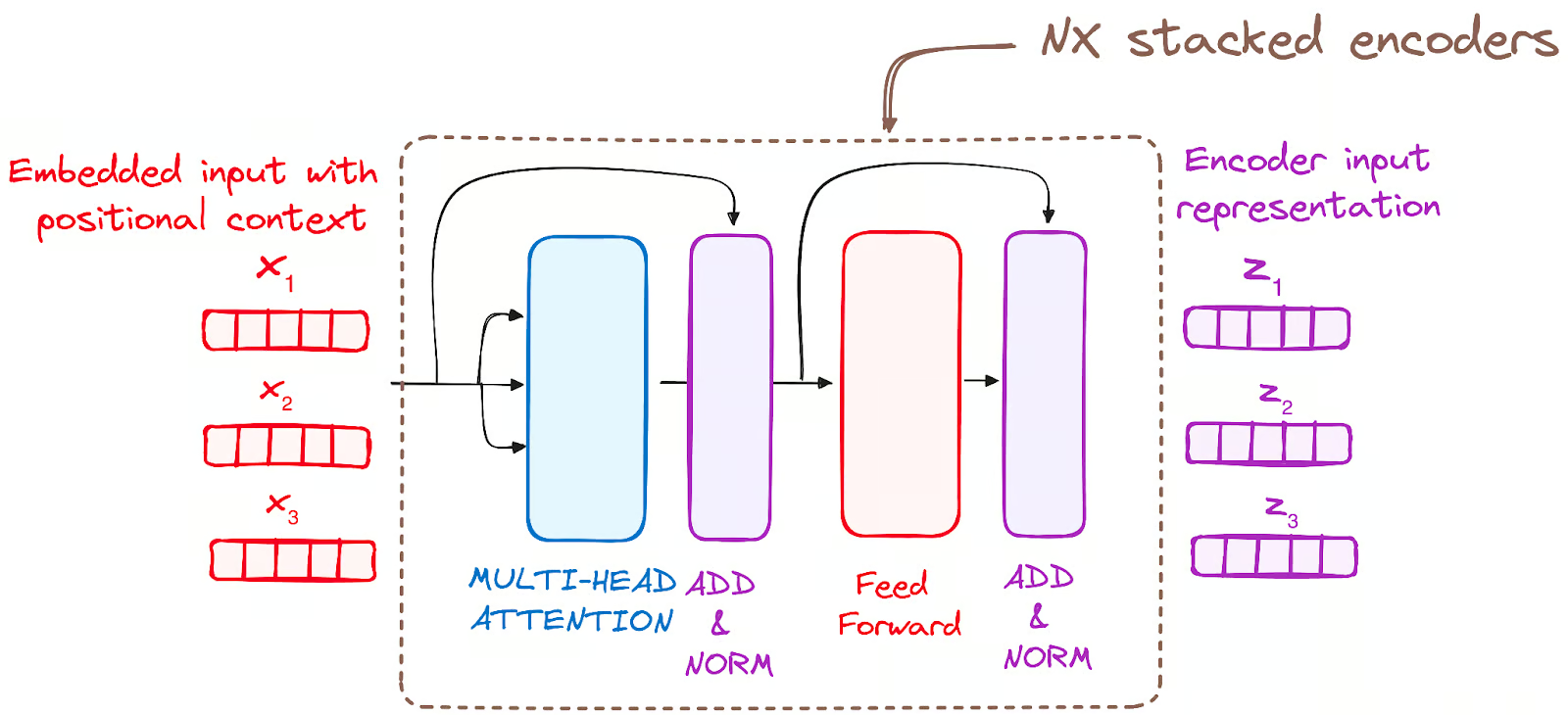
Input tensor is split into \(h\) segments along the embedding dimension and fed to individual self-attention layer
Each attention layer uses different \(\mathbf{W}_Q,\mathbf{W}_K,\mathbf{W}_V\) matrices to capture different context like syntax, long-range dependencies and local neighbors
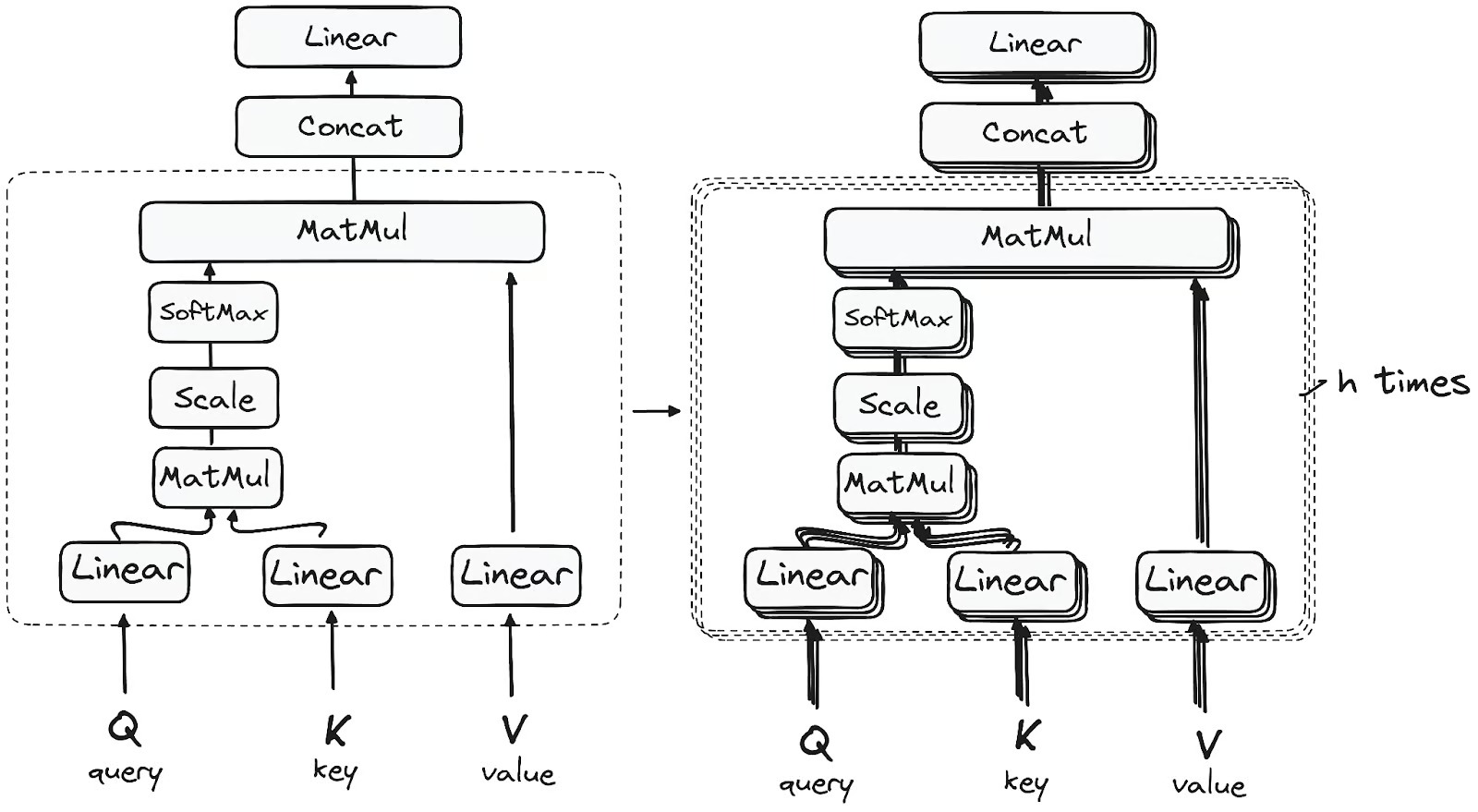
For additional refinement
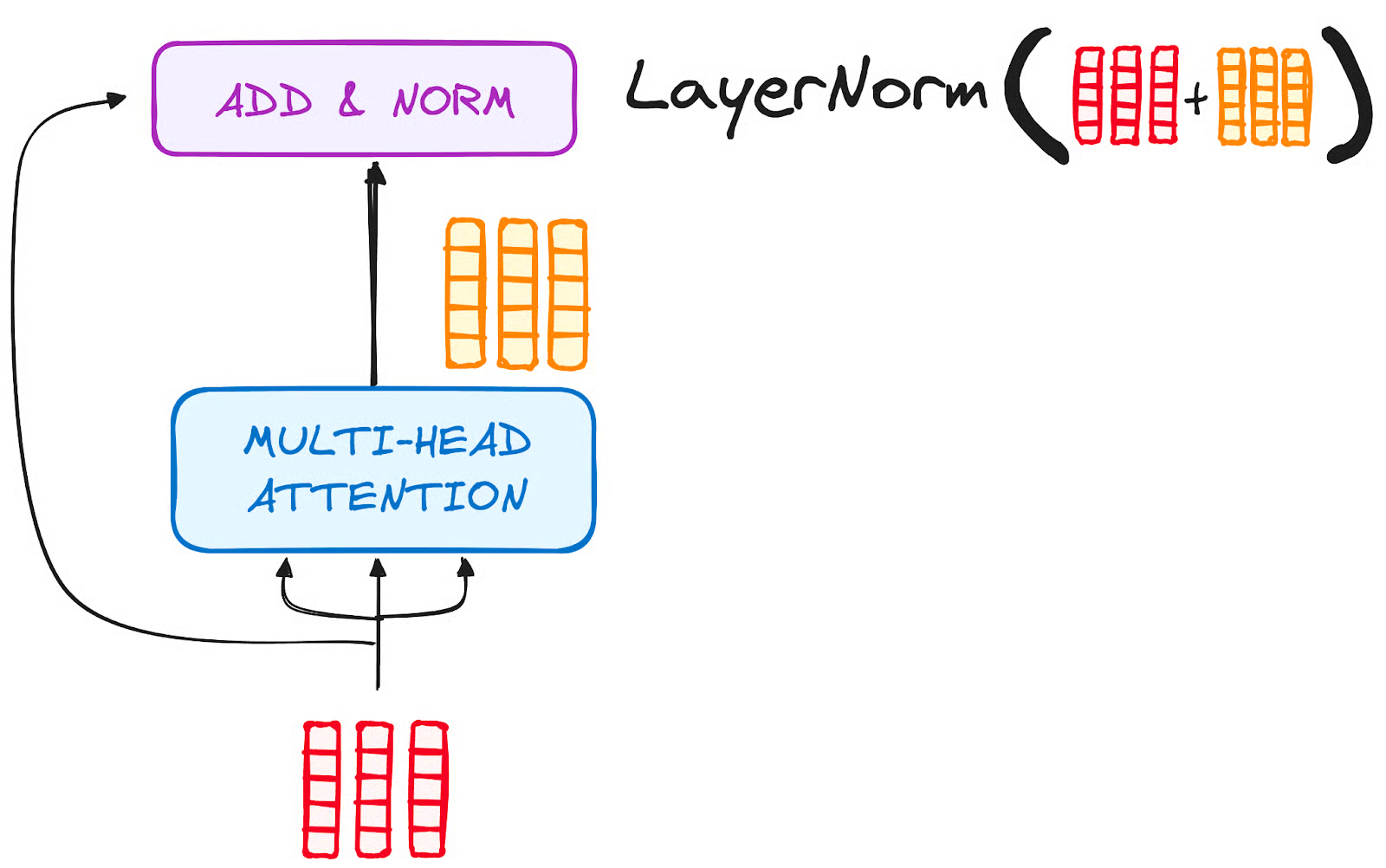
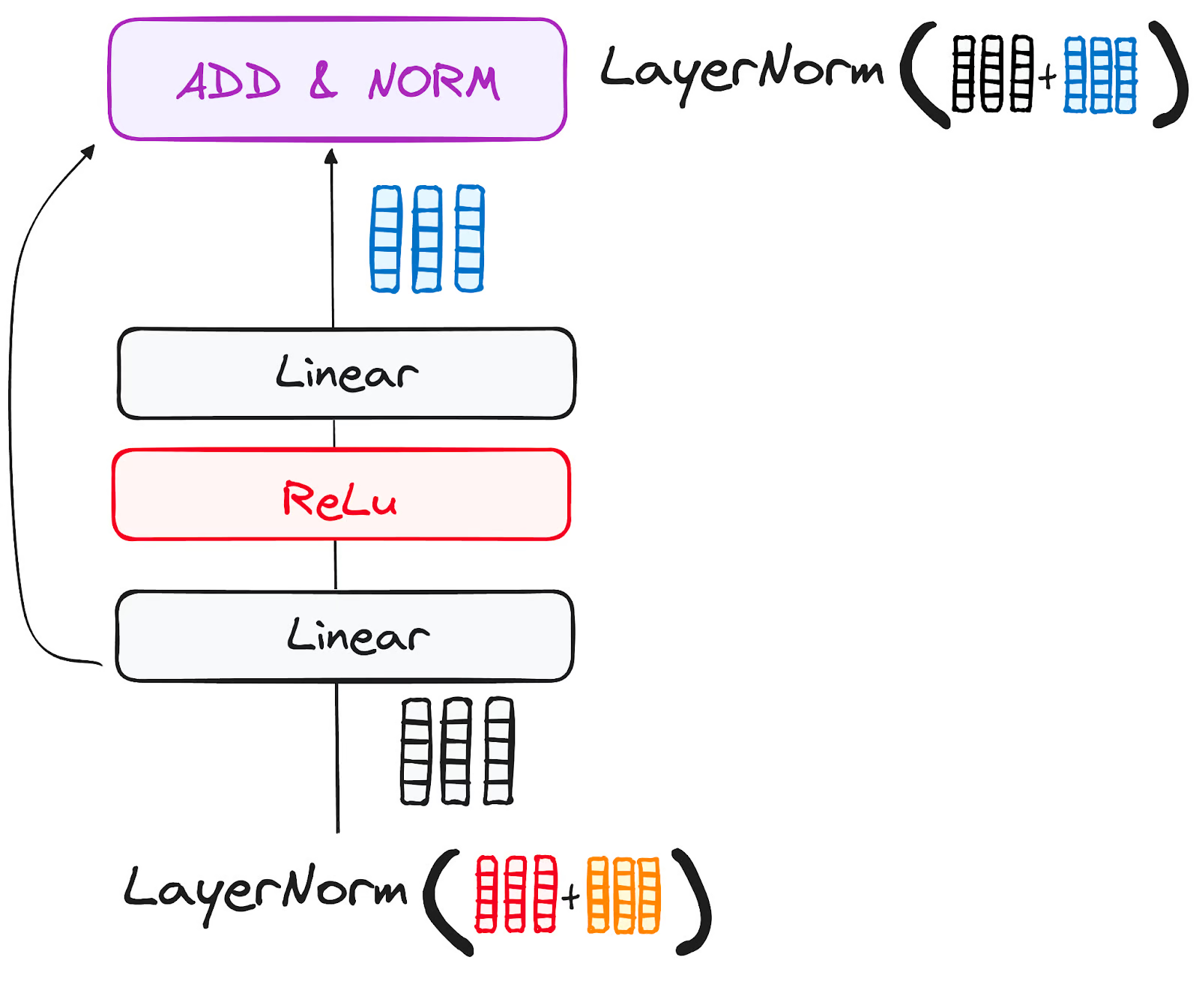
Here also, residual connections and Layer normalization
Then the output of encoder is sent to decoder part
Overview of a single decoder layer
Each has 2 multi-headed attention mechanism but slightly different
Then the output of decoder is passed through softmax layer to get probability of word that comes next
Output embedding and positional encodings are similar to that in encoder part
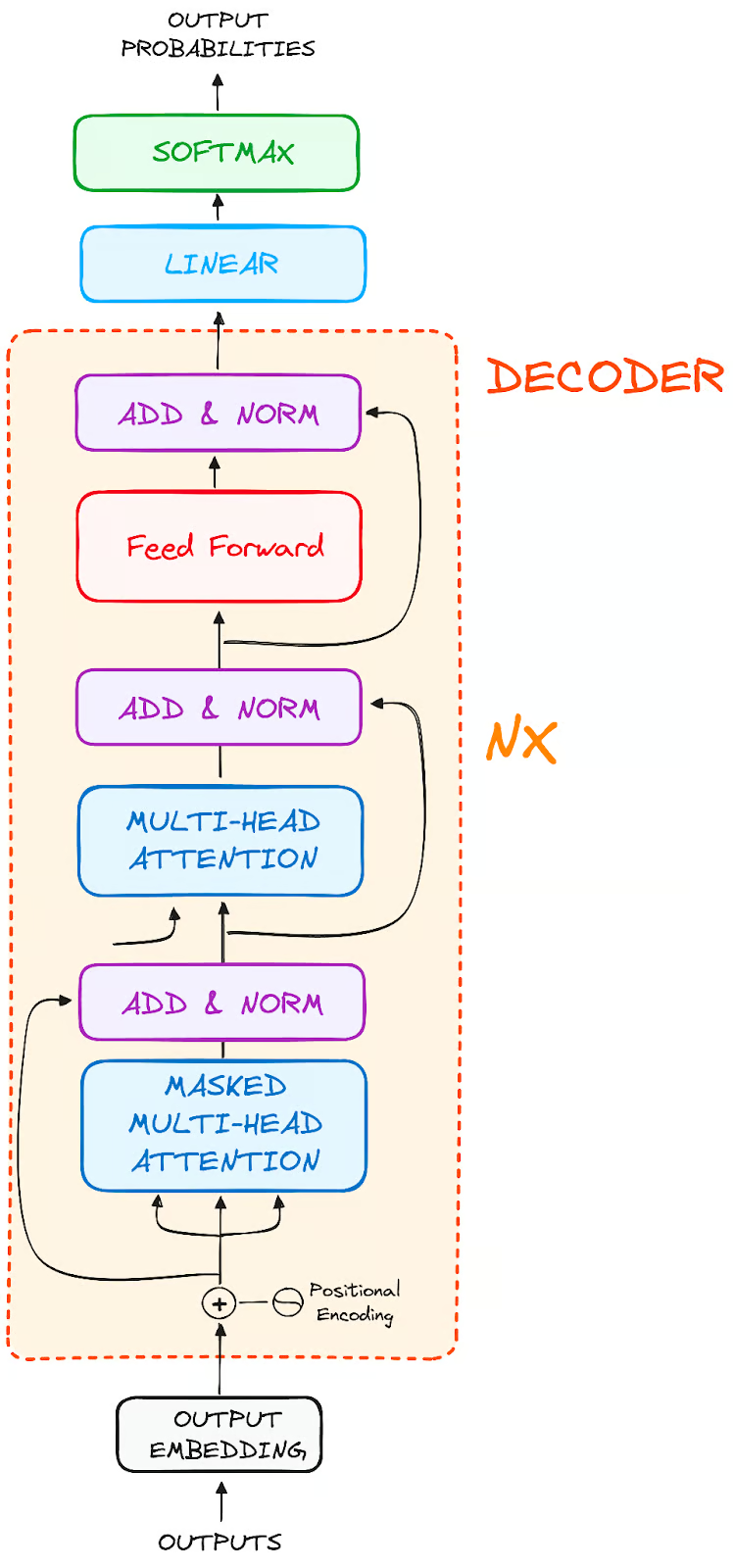
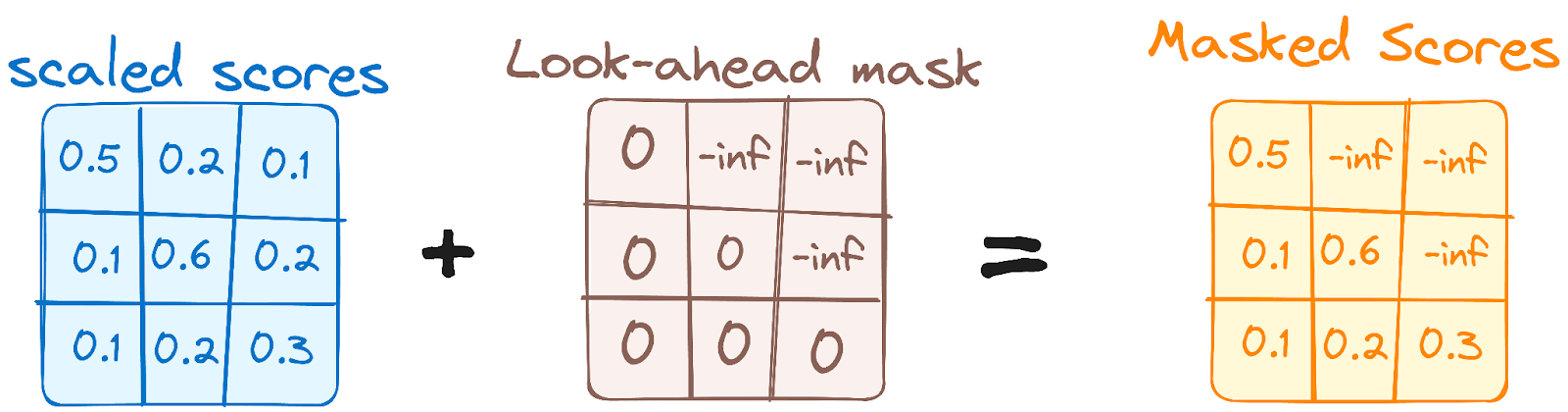
This prevents the positions/tokens from attending subsequent positions/tokens
Each has 2 multi-headed attention mechanism but slightly different
This mask ensures that the prediction for particular position is dependent only on previous positions.
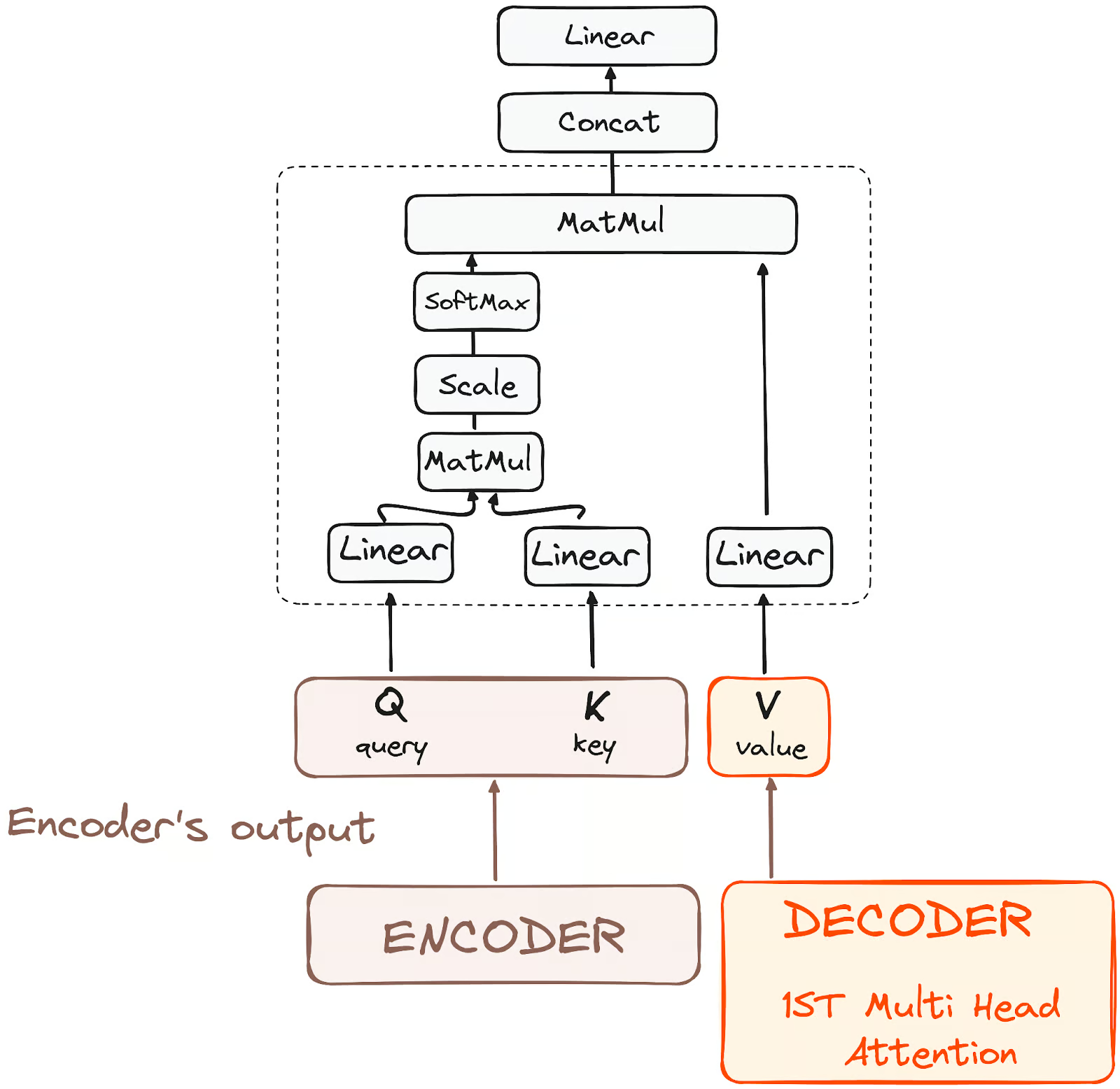
This is where the input from encoder comes in.
Here, the correlation between vocabulary of two languages is determined
This will be followed by the feedforward network, where the interpretation in translation happens
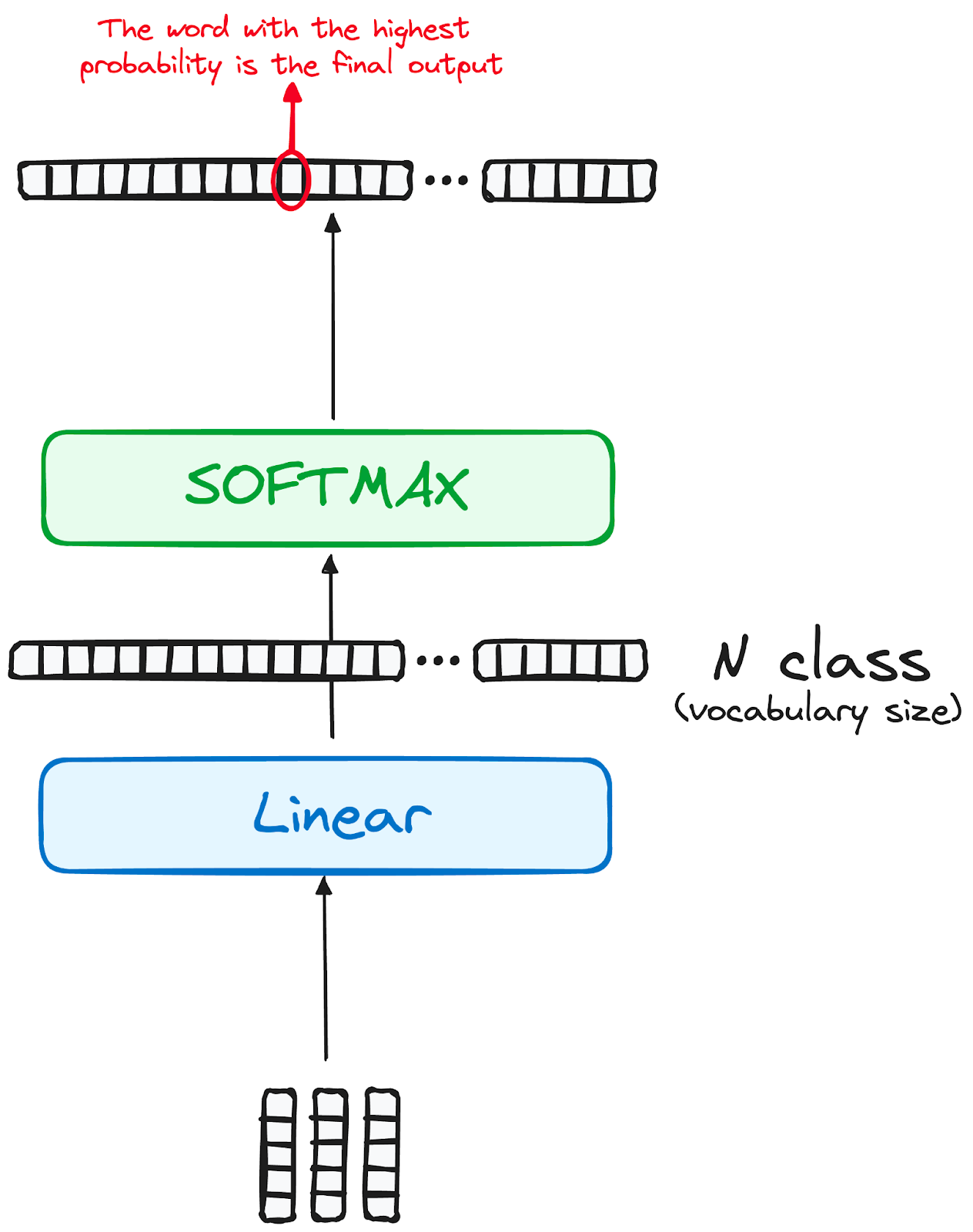
The final output is passed through softmax acitvation function
It generates the probability of the next word in sequence
The probability is looked against the words in the vocabulary of second language
RNNs and its variants fail to interpret long sequences and they are under-utilizing the computing resources
Attention mechanism is used to interpret the context of short/long sequences. It is the core of Transformer networks.
Transformer also has encoder and decoder type architecture.
Transformer takes entire sequence at once as input. It does not have recurrence feature like in RNN.
Multi-headed attention mechanism parallelizes training and captures more context from the sequence.
Position encoding and word embedding are used for proper transformation of words to vectors. Hence, the name Transformer networks.
https://builtin.com/artificial-intelligence/transformer-neural-network
https://www.datacamp.com/tutorial/building-a-transformer-with-py-torch
https://www.datacamp.com/tutorial/building-a-transformer-with-py-torch
“Attention is all you need” paper by Vaswani et al (2017).

Transformers